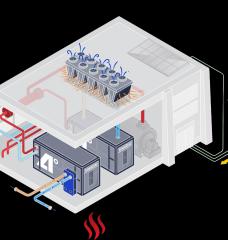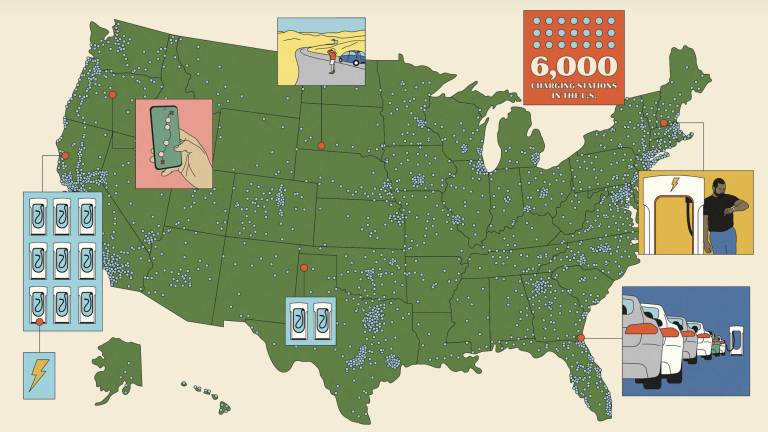
The United States has around 150,000 fuel stations to refill its fleet of fossil-fuel-burning vehicles. Despite the rapid growth of all-electric vehicles in America—400,000 of them were sold in 2021, up from barely 10,000 in 2012—the country has only 6,000 DC fast electric charging stations, the kind that can rapidly juice up a battery-powered car. (It has more than 48,000 charging stations of all kinds.)
A glance at America’s charging map reveals an abundance of charging deserts. This makes sense, as EVs still represent less than 3% of new car sales. Large cities have a growing number of fast chargers, but not nearly enough to accommodate a major influx of EVs. Away from cities, these chargers are strung along interstate highways closely enough to allow electric cars safe passage. Otherwise, they are nearly nonexistent in rural America. And EV stations have a problem that gas stations don’t: “Even the fastest Tesla supercharger is still going to take 15 minutes to put a couple hundred miles on the vehicle,” says Jeremy Michalek, a professor at Carnegie Mellon University and director of its Vehicle Electrification Group.
Michalek says American charging infrastructure lags far behind what’s needed for the whole country to transition to electric driving. On the bright side, there is time to catch up, because not all Americans will embrace EVs at once. Most early adopters were those with access to a charger at home in their garage or parking space. Those owners can wake up with a full battery and only need to rely on public chargers when they leave town on an extended trip. But as the country gets to higher levels of EV adoption, the current infrastructure won’t be enough. That is why Michalek says the US needs to prioritize bulking up the number of chargers at rest stops along well-traveled highways, especially as more people pile into electric cars for summertime road trips.
“As we get to higher levels of EV adoption, if we don’t have enough chargers for peak demand, the wait times are going to be unlike what we see with gas stations,” he says.
Read the full story at MIT Technology Review.