Photo Credit
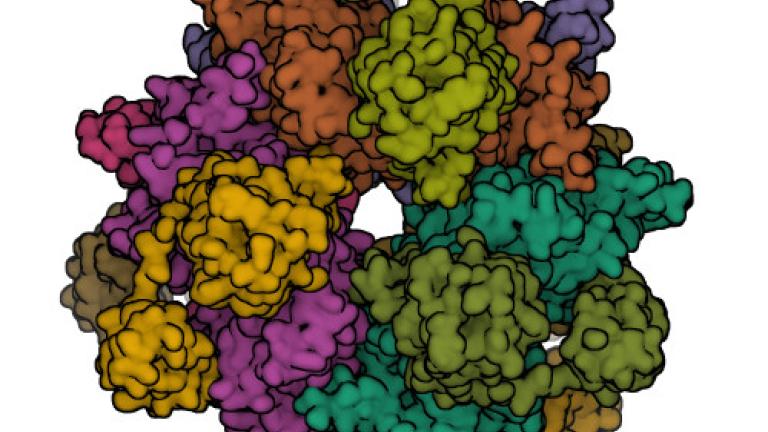
Researchers used directed evolution strategies to engineering a new carbon-dioxide-fixing enzyme, glycolyl-CoA carboxylase, or GCC, which may improve the efficiency of photosynthesis and carbon capture. (Image from the RCSB PDB of PDB ID 6YBQ.)
This Advanced Undergraduate Biology Seminar covers the many ways in which we have realized evolution in the laboratory toward functional biomolecules, such as protein and nucleic-acid-based therapeutics, enzymes that catalyze production of synthetic drugs, and carbon-dioxide capture molecules to lessen the impact of climate change. Students will both become familiar with the field of directed molecular evolution and learn how to critically analyze primary research papers, design research experiments, and present data relating to molecular biology and evolution. The importance of directed evolution in biomedical and biotechnological careers, both academic and industrial, is highlighted.
Instructors: Dr. Megan Kizer, Dr. Robbie Wilson






