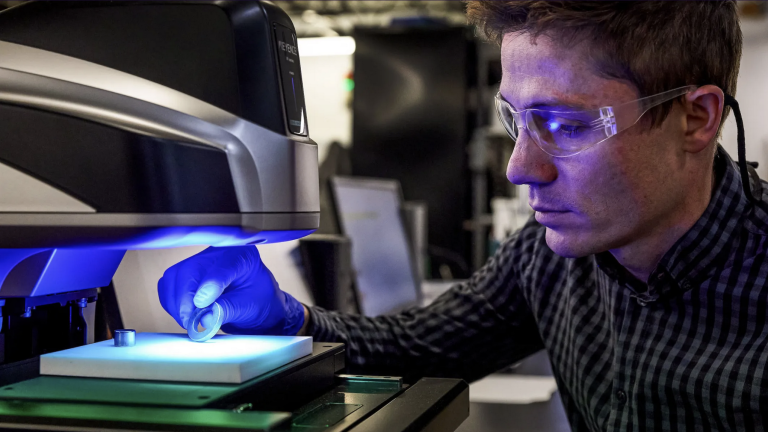
The motor in your vacuum cleaner and the one in your electric vehicle likely have at least one thing in common: they both rely on powerful permanent magnets to function. And the materials for those magnets could soon be in short supply.
Permanent magnets can maintain a magnetic field on their own without an electric charge. They’re commonly used in motors, making them spin when an electric field is applied. The permanent magnets used in high-end motors today are built using a class of materials called rare earth metals. Demand for these materials is expected to skyrocket in the coming decades, fueled in particular by the growth of electric vehicles and wind turbines. As mines and processing facilities struggle to keep up, supplies may stretch thin.
One Minnesota startup has been working to address this looming shortage. Niron Magnetics is building a large-scale manufacturing facility to produce iron nitride, a magnetic material derived from common elements, while also working to improve the material’s properties so that it can be used in stronger magnets to power more products. The results may help address yet another coming supply crunch that threatens to slow down action on climate change.