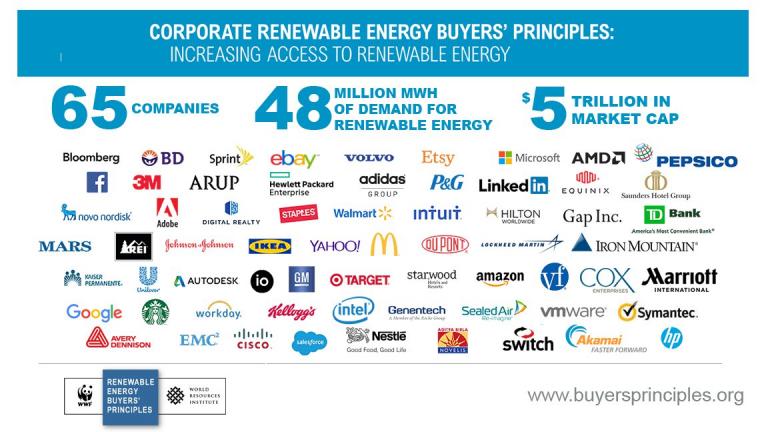
Often lost in the conversation about responding to the Trump administration's backing out the Paris Accords is where "markets" fit. As several posts on ClimateX have made clear, bottom-line-oriented investors - whether in red or blue states - are diving headlong into renewables. A recent Green Biz article "The growth of corporate clean energy in 6 charts" shows how
In markets where wind and solar power have become cost competitive, utilities have more economic incentives to add renewable energy. Renewable resources just offer a great low price for the next 20 years — without the risks of fossil fuel price spikes. Further on the demand side, 90 companies have committed to 100 percent renewable power. Clean energy and greenhouse gas reduction targets are the norm for Fortune 500 and Fortune 100 companies. WWF and Ceres’ Power Forward 3.0 report shows that almost half of the Fortune 500 and a majority of the Fortune 100 have climate and energy targets.
It's becoming clear that States whose utilities offer renewable energy options (including a "green tariff") are more competitive when attracting high-growth corporate business, and that trend is expected to continue. Local and especially state-level goverments can help, as the Power Forward report articulates by establishing long-term low-carbon polices that will help companies meet their clean energy targets while also helping the US meet its carbon-reducing commitments - with or without federal participation in the Paris Accords.
Seems to me that "market forces" play a critical role, but only effective within an approach that includes all the other critical players in the system.






