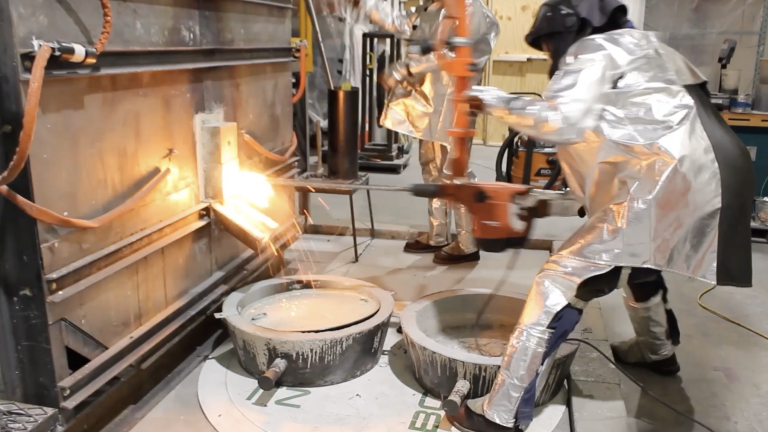
When you climb up a set of stairs to look over Boston Metal’s newest project, it becomes clear just how big a job it is to cut steel’s climate impact.
The impressive new installation is a pilot reactor that the startup will use to make emissions-free steel. It’s about the size of a school bus, set down into the floor of the research facility; the stairs, with freshly painted yellow railings, lead to the top. But in the steel industry, which produces nearly 2 billion tons per year, this setup’s potential output is a drop in the bucket.
Industrial steelmaking spits out about two tons of carbon dioxide emissions for every ton of steel produced—adding up to nearly 10% of such emissions worldwide. The global steel market is expected to grow about 30% by 2050, the date by which some of the largest steelmakers have pledged to reach net-zero emissions. Unless major changes come to the industry, and fast, that goal might be out of reach.
Boston Metal’s new reactor, recently installed at its headquarters just north of Boston, is a significant step on the company’s journey to going commercial. Since its founding in 2013, the startup has developed a process to make green steel, working out the details in smaller vessels. The new reactor, along with a coming fundraising round, represents the next leap for the company as it tries to scale up.
Read the full story at MIT Technology Review.