Next year, New Belgium Brewing will swap out one of the four natural-gas-powered boilers at its main brewing facility in Fort Collins, Colorado, for an electrified version designed to cut greenhouse-gas emissions.
The modular, 650-kilowatt pilot boiler system was developed by AtmosZero, a startup also based in Fort Collins and coming out of stealth today.
“To decarbonize industry, we must decarbonize heat,” says Addison Stark, chief executive and cofounder of the startup.
Indeed, heat production from industry may account for around 10% of global carbon dioxide pollution. The sector relies heavily on steam to transfer heat, sterilize equipment and goods, and separate chemicals. Globally, the practice could generate more than 2 billion tons of carbon dioxide pollution per year, according to an earlier analysis by Stark and a colleague.
New Belgium Brewing, best known for producing Fat Tire ale, uses vast amounts of steam to fine-tune the temperatures within its boil kettles, helping to draw out flavors from hops and grains at crucial points of the beer-making process.
Electric boilers that can draw power mostly from renewables like solar and wind do exist and are already used in manufacturing. But they generally rely on resistive heating, which produces heat by passing an electric current through a conductive material, or the water in the boiler. That sucks up a lot of electricity and pushes up costs, which has prevented such devices from grabbing much market share to date, says Stark, previously a fellow and acting director at ARPA-E, the US Department of Energy’s advanced research arm.
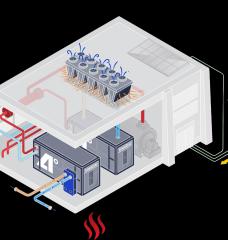
Instead, AtmosZero leans on heat pump technology, which uses electricity to circulate refrigerants with low boiling points through a closed loop. The device draws in heat from the surrounding air, uses a compressor to increase the temperature of the refrigerant enough to boil water, and then transfers that thermal energy through a heat exchanger into a vessel that produces steam.
Heat pumps can be far more efficient than products that rely on resistive heating because, as MIT Technology Review’s Casey Crownhart laid out in an earlier explainer, most of the electricity is used to gather heat and move it around, rather than producing it directly.
Stark says that a commercial version of the company’s device could be up to twice as efficient as resistive boilers.