Placing a lit candle in a window to welcome friends and strangers is an old Irish tradition that took on greater significance when Mary Robinson was elected president of Ireland in 1990. At the time, Robinson placed a lamp in Áras an Uachtaráin — the official residence of Ireland’s presidents — noting that the Irish diaspora and all others are always welcome in Ireland. Decades later, a lit lamp remains in a window in Áras an Uachtaráin.
The symbolism of Robinson’s lamp was shared by Hashim Sarkis, dean of the MIT School of Architecture and Planning (SA+P), at the school’s graduation ceremony in May, where Robinson addressed the class of 2025. To replicate the generous intentions of Robinson’s lamp and commemorate her visit to MIT, Sarkis commissioned a unique lantern as a gift for Robinson. He commissioned an identical one for his office, which is in the front portico of MIT at 77 Massachusetts Ave.
“The lamp will welcome all citizens of the world to MIT,” says Sarkis.
No ordinary lantern
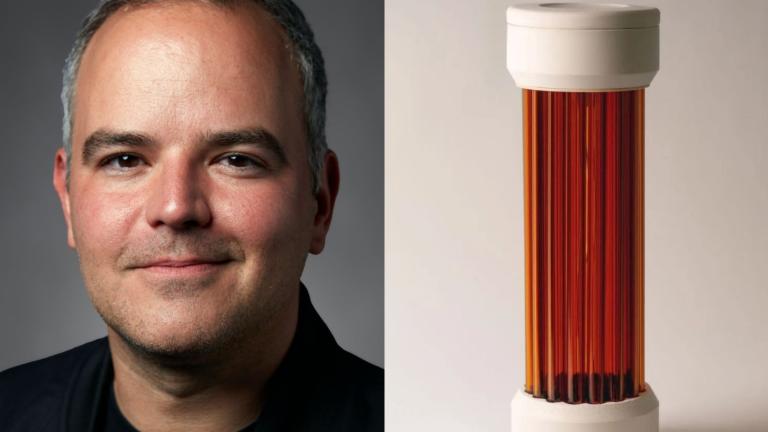
The bespoke lantern was created by Marcelo Coelho SM ’08, PhD ’12, director of the Design Intelligence Lab and associate professor of the practice in the Department of Architecture.
One of several projects in the Geoletric research at the Design Intelligence Lab, the lantern showcases the use of geopolymers as a sustainable material alternative for embedded computers and consumer electronics.
“The materials that we use to make computers have a negative impact on climate, so we’re rethinking how we make products with embedded electronics — such as a lamp or lantern — from a climate perspective,” says Coelho.
Consumer electronics rely on materials that are high in carbon emissions and difficult to recycle. As the demand for embedded computing increases, so too does the need for alternative materials that have a reduced environmental impact while supporting electronic functionality.
The Geolectric lantern advances the formulation and application of geopolymers — a class of inorganic materials that form covalently bonded, non-crystalline networks. Unlike traditional ceramics, geopolymers do not require high-temperature firing, allowing electronic components to be embedded seamlessly during production.
Geopolymers are similar to ceramics, but have a lower carbon footprint and present a sustainable alternative for consumer electronics, product design, and architecture. The minerals Coelho uses to make the geopolymers — aluminum silicate and sodium silicate — are those regularly used to make ceramics.
“Geopolymers aren’t particularly new, but are becoming more popular,” says Coelho. “They have high strength in both tension and compression, superior durability, fire resistance, and thermal insulation. Compared to concrete, geopolymers don’t release carbon dioxide. Compared to ceramics, you don’t have to worry about firing them. What’s even more interesting is that they can be made from industrial byproducts and waste materials, contributing to a circular economy and reducing waste.”
The lantern is embedded with custom electronics that serve as a proximity and touch sensor. When a hand is placed over the top, light shines down the glass tubes.
The timeless design of the Geoelectric lantern — minimalist, composed of natural materials — belies its future-forward function. Coelho’s academic background is in fine arts and computer science. Much of his work, he says, “bridges these two worlds.”
Working at the Design Intelligence Lab with Coelho on the lanterns are Jacob Payne, a graduate architecture student, and Jean-Baptiste Labrune, a research affiliate.
A light for MIT
A few weeks before commencement, Sarkis saw the Geoelectric lantern in Palazzo Diedo Berggruen Arts and Culture in Venice, Italy. The exhibition, a collateral event of the Venice Biennale’s 19th International Architecture Exhibition, featured the work of 40 MIT architecture faculty.
The sustainability feature of Geolectric is the key reason Sarkis regarded the lantern as the perfect gift for Robinson. After her career in politics, Robinson founded the Mary Robinson Foundation — Climate Justice, an international center addressing the impacts of climate change on marginalized communities.
The third iteration of Geolectric for Sarkis’ office is currently underway. While the lantern was a technical prototype and an opportunity to showcase his lab’s research, Coelho — an immigrant from Brazil — was profoundly touched by how Sarkis created the perfect symbolism to both embody the welcoming spirit of the school and honor President Robinson.
“When the world feels most fragile, we need to urgently find sustainable and resilient solutions for our built environment. It’s in the darkest times when we need light the most,” says Coelho.